 Yandere Boyfriend LC
@sharkfucker96 :
Yandere Boyfriend LC
@sharkfucker96 : Polygon ✔ @Polygon :
Polygon ✔ @Polygon : David Risney
@David_Risney :
David Risney
@David_Risney : David Risney
@David_Risney :
David Risney
@David_Risney : Eric Lawrence
@ericlaw :
Eric Lawrence
@ericlaw : Mathematically speaking, any two ducks are already in a row. In order to get your
ducks in a row, own exactly two ducks.
Mathematically speaking, any two ducks are already in a row. In order to get your
ducks in a row, own exactly two ducks.
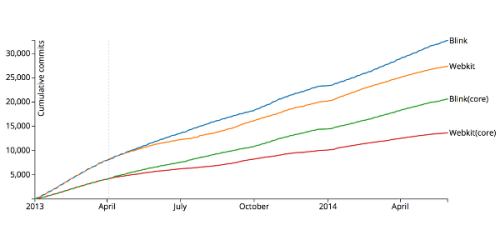
A high-profile fork: one year of Blink and Webkit
Some stats and analysis at a very high level of the Blink fork from Webkit.
URI Design & Ownership - On the issues with and alternatives to requiring well known filenames and extensions in URIs. You must love the draft’s URI.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION]
"Fitbit Connect.exe"=dword:000022b8
Param([Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$Path);
$excel = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$xlWindows=2
$xlDelimited=1 # 1 = delimited, 2 = fixed width
$xlTextQualifierDoubleQuote=1 # 1= doublt quote, -4142 = no delim, 2 = single quote
$consequitiveDelim = $False;
$tabDelim = $False;
$semicolonDelim = $False;
$commaDelim = $True;
$StartRow=1
$Semicolon=$True
$excel.visible=$true
$excel.workbooks.OpenText($Path,$xlWindows,$StartRow,$xlDelimited,$xlTextQualifierDoubleQuote,$consequitiveDelim,$tabDelim,$semicolonDelim, $commaDelim);My second completed app for the Windows Store was Words with Hints a companion to Words with Friends or other Scrabble like games that gives you *ahem* hints. You provide your tiles and optionally letters placed in a line on the board and Words with Hints gives you word options.
I wrote this the first time by building a regular expression to check against my dictionary of words which made for a slow app on the Surface. In subsequent release of the app I now spawn four web workers (one for each of the Surface's cores) each with its own fourth of my dictionary. Each fourth of the dictionary is a trie which makes it easy for me to discard whole chunks of possible combinations of Scrabble letters as I walk the tree of possibilities.
The dictionaries are large and takes a noticeable amount of time to load on the Surface. The best performing mechanism I found to load them is as JavaScript source files that simply define their portion of the dictionary on the global object and synchronously (only on the worker so not blocking the UI thread). Putting them into .js files means they take advantage of bytecode caching making them load faster. However because the data is mostly strings and not code there is a dramatic size increase when the app is installed. The total size of the four dictionary .js files is about 44Mb. The bytecode cache for the dictionary files is about double that 88Mb meaning the dictionary plus the bytecode cache is 132Mb.
To handle the bother of postMessage communication and web workers this was the first app in which I used my promise MessagePort project which I'll discuss more in the future.
This is the first app in which I used the Microsoft Ad SDK. It was difficult to find the install for the SDK and difficult to use their website, but once setup, the Ad SDK was easy to import into VS and easy to use in my app.
Wrote some scripts that produce .cmdtree files. Nice to find this format definition.
Level 5 of the Stripe CTF revolved around a design issue in an OpenID like protocol.
def authenticated?(body)
body =~ /[^\w]AUTHENTICATED[^\w]*$/
end
...
if authenticated?(body)
session[:auth_user] = username
session[:auth_host] = host
return "Remote server responded with: #{body}." \
" Authenticated as #{username}@#{host}!"This level is an implementation of a federated identity protocol. You give it an endpoint URI and a username and password, it posts the username and password to the endpoint URI, and if the response is 'AUTHENTICATED' then access is allowed. It is easy to be authenticated on a server you control, but this level requires you to authenticate from the server running the level. This level only talks to stripe CTF servers so the first step is to upload a document to the level 2 server containing the text 'AUTHENTICATED' and we can now authenticate on a level 2 server. Notice that the level 5 server will dump out the content of the endpoint URI and that the regexp it uses to detect the text 'AUTHENTICATED' can match on that dump. Accordingly I uploaded an authenticated file to
https://level02-2.stripe-ctf.com/user-ajvivlehdt/uploads/authenticatedhttps://level05-1.stripe-ctf.com/user-qtoyekwrod/?pingback=https%3A%2F%2Flevel02-2.stripe-ctf.com%2Fuser-ajvivlehdt%2Fuploads%2Fauthenticated&username=a&password=aI didn't see any particular code review red flags, really the issue here is that the regular expression testing for 'AUTHENTICATED' is too permisive and the protocol itself doesn't do enough. The protocol requires only a set piece of common literal text to be returned which makes it easy for a server to accidentally fall into authenticating. Having the endpoint URI have to return variable text based on the input would make it much harder for a server to accidentally authenticate.
Stripe's web security CTF's Level 1 and level 2 of the Stripe CTF had issues with missing input validation solutions described below.
$filename = 'secret-combination.txt';
extract($_GET);
if (isset($attempt)) {
$combination = trim(file_get_contents($filename));
if ($attempt === $combination) {The issue here is the usage of the extract php method which extracts name value pairs from the map input parameter and creates corresponding local variables. However this code uses $_GET which contains a map of name value pairs passed in the query of the URI. The expected behavior is to get an attempt variable out, but since no input validation is done I can provide a filename variable and overwrite the value of $filename. Providing an empty string gives an empty string $combination which I can match with an empty string $attempt. So without knowing the combination I can get past the combination check.
Code review red flag in this case was the direct use of $_GET with no validation. Instead of using extract the developer could try to extract specifically the attempt variable manually without using extract.
$dest_dir = "uploads/";
$dest = $dest_dir . basename($_FILES["dispic"]["name"]);
$src = $_FILES["dispic"]["tmp_name"];
if (move_uploaded_file($src, $dest)) {
$_SESSION["dispic_url"] = $dest;
chmod($dest, 0644);
echo "Successfully uploaded your display picture.
";
}
This code accepts POST uploads of images but with no validation to ensure it is not an arbitrary file. And even though it uses chmod to ensure the file is not executable, things like PHP don't require a file to be executable in order to run them. Accordingly, one can upload a PHP script, then navigate to that script to run it. My PHP script dumped out the contents of the file we're interested in for this level:
Code review red flags include manual file management, chmod, and use of file and filename inputs without any kind of validation. If this code controlled the filename and ensured that the extension was one of a set of image extensions, this would solve this issue. Due to browser mime sniffing its additionally a good idea to serve a content-type that starts with "image/" for these uploads to ensure browsers treat these as images and not sniff for script or HTML.
 [Testing Cat-Human Translator] Scientist: Cat, what is your name? Cat: I AM KANG THE
DESTROYER Owner: It's not working. His name is Socks.
[Testing Cat-Human Translator] Scientist: Cat, what is your name? Cat: I AM KANG THE
DESTROYER Owner: It's not working. His name is Socks.
 OH: "take me down to concurrency city where green pretty is grass the girls the and
are"
OH: "take me down to concurrency city where green pretty is grass the girls the and
are"