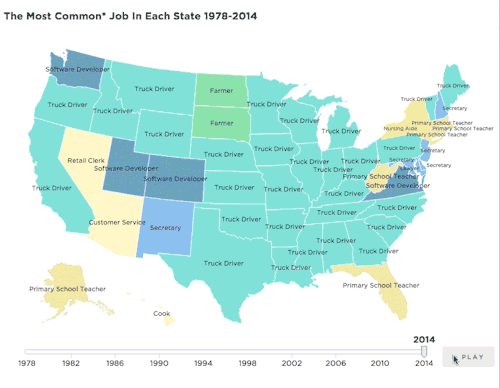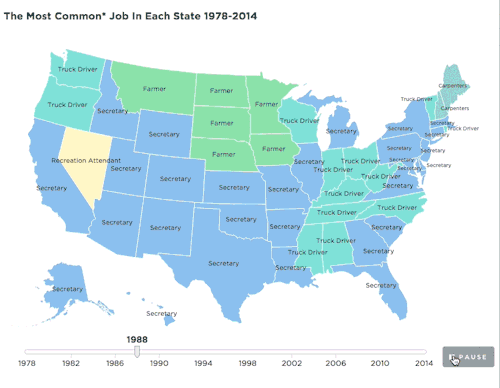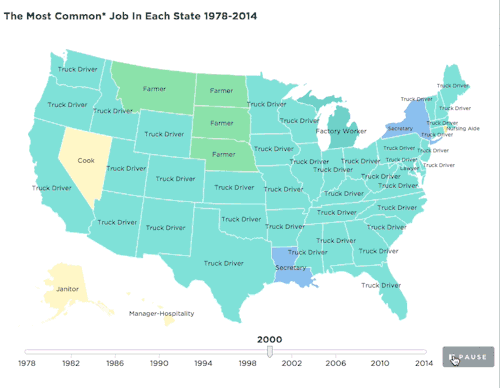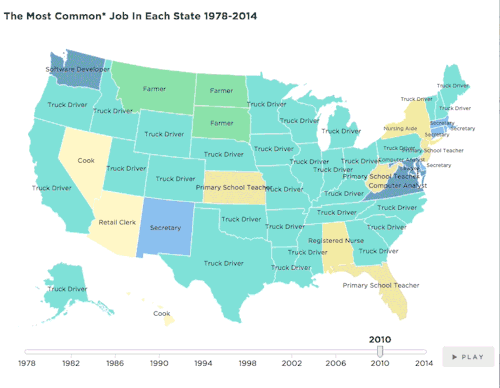
Summary
The Modern SDK contains some URI related functionality as do libraries available in particular projection languages. Unfortunately, collectively these APIs do not cover all scenarios in all
languages. Specifically, JavaScript and C++ have no URI building APIs, and C++ additionally has no percent-encoding/decoding APIs.
|
WinRT (JS and
C++)
|
JS Only
|
C++ Only
|
.NET Only
|
|
Parse
|
|
|
|
|
|
Build
|
|
|
|
|
|
Normalize
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equality
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relative
resolution
|
|
|
|
|
|
Encode data for
including in URI property
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decode data extracted
from URI property
|
|
|
|
|
|
Build Query
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parse Query
|
|
|
|
|
The Windows.Foudnation.Uri type is not projected into .NET modern applications. Instead those applications use System.Uri and the
platform ensures that it is correctly converted back and forth between Windows.Foundation.Uri as appropriate. Accordingly the column marked WinRT above is applicable
to JS and C++ modern applications but not .NET modern applications. The only entries above applicable to .NET are the .NET Only column and the WwwFormUrlDecoder in the bottom left which is available to .NET.
Scenarios
Parse
This functionality is provided by the WinRT API Windows.Foundation.Uri in C++ and JS, and by System.Uri in .NET.
Parsing a URI pulls it apart into its basic components without decoding or otherwise modifying the contents.
var uri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/path%20segment1/path%20segment2?key1=value1&key2=value2");
console.log(uri.path);// /path%20segment1/path%20segment2
WsDecodeUrl (C++)
WsDecodeUrl is not suitable for general purpose URI parsing. Use Windows.Foundation.Uri
instead.
Build (C#)
URI building is only available in C# via System.UriBuilder.
URI building is the inverse of URI parsing: URI building allows the developer to specify the value of basic components of a URI and the API assembles them into a URI.
To work around the lack of a URI building API developers will likely concatenate strings to form their URIs. This can lead to injection bugs if
they don’t validate or encode their input properly, but if based on trusted or known input is unlikely to have issues.
Uri originalUri = new Uri("http://example.com/path1/?query");
UriBuilder uriBuilder = new UriBuilder(originalUri);
uriBuilder.Path = "/path2/";
WsEncodeUrl (C++)
WsEncodeUrl, in addition to building a URI from components also does some encoding. It encodes non-US-ASCII characters
as UTF8, the percent, and a subset of gen-delims based on the URI property: all :/?#[]@ are percent-encoded except :/@ in the path and
:/?@ in query and fragment.
Accordingly, WsEncodeUrl is not suitable for general purpose URI building. It is acceptable to use in the following
cases:
- You’re building a URI out of non-encoded URI properties and don’t care about the difference between encoded and decoded characters. For instance
you’re the only one consuming the URI and you uniformly decode URI properties when consuming – for instance using WsDecodeUrl to consume the URI.
- You’re building a URI with URI properties that don’t contain any of the characters that WsEncodeUrl encodes.
Normalize
This functionality is provided by the WinRT API Windows.Foundation.Uri in C++ and JS and by System.Uri in .NET. Normalization is applied during construction of the Uri object.
URI normalization is the application of URI normalization rules (including DNS normalization, IDN normalization, percent-encoding normalization, etc.) to the input URI.
var normalizedUri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("HTTP://EXAMPLE.COM/p%61th foo/");
console.log(normalizedUri.absoluteUri); // http://example.com/path%20foo/
This is modulo Win8 812823 in which the Windows.Foundation.Uri.AbsoluteUri property returns a normalized IRI not a normalized URI. This bug does not affect System.Uri.AbsoluteUri which returns a normalized URI.
Equality
This functionality is provided by the WinRT API Windows.Foundation.Uri in C++ and JS and by System.Uri in .NET.
URI equality determines if two URIs are equal or not necessarily equal.
var uri1 = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("HTTP://EXAMPLE.COM/p%61th foo/"),
uri2 = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/path%20foo/");
console.log(uri1.equals(uri2)); // true
Relative resolution
This functionality is provided by the WinRT API Windows.Foundation.Uri in C++ and JS and by System.Uri in .NET
Relative resolution is a function that given an absolute URI A and a relative URI B, produces a new absolute URI C. C is the combination of A and B
in which the basic components specified in B override or combine with those in A under rules specified in RFC 3986.
var baseUri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/index.html"),
relativeUri = "/path?query#fragment",
absoluteUri =
baseUri.combineUri(relativeUri);
console.log(baseUri.absoluteUri); // http://example.com/index.html
console.log(absoluteUri.absoluteUri); // http://example.com/path?query#fragment
Encode data for including in URI property
This functionality is available in JavaScript via encodeURIComponent and in C# via System.Uri.EscapeDataString. Although the two methods
mentioned above will suffice for this purpose, they do not perform exactly the same operation.
Additionally we now have Windows.Foundation.Uri.EscapeComponent in WinRT, which is available in JavaScript and C++ (not C# since it doesn’t have access to
Windows.Foundation.Uri). This is also slightly different from the previously mentioned mechanisms but works best for
this purpose.
Encoding data for inclusion in a URI property is necessary when constructing a URI from data. In all the above cases the developer is dealing with
a URI or substrings of a URI and so the strings are all encoded as appropriate. For instance, in the parsing example the path contains “path%20segment1” and not “path segment1”. To construct a URI one must first construct the basic components of the URI which involves encoding the data.
For example, if one wanted to include “path segment / example” in the path of a URI, one must percent-encode the ‘ ‘ since it is not allowed in a URI, as well as the
‘/’ since although it is allowed, it is a delimiter and won’t be interpreted as data unless encoded.
If a developer does not have this API provided they can write it themselves. Percent-encoding methods appear simple to write, but the difficult
part is getting the set of characters to encode correct, as well as handling non-US-ASCII characters.
var uri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com" +
"/" + Windows.Foundation.Uri.escapeComponent("path segment / example") +
"?key=" + Windows.Foundation.Uri.escapeComponent("=&?#"));
WsEncodeUrl (C++)
In addition to building a URI from components, WsEncodeUrl also percent-encodes some characters. However the API is not recommend for this scenario given the particular set of characters that are encoded and the convoluted nature in which a developer
would have to use this API in order to use it for this purpose.
There are no general purpose scenarios for which the characters WsEncodeUrl encodes make sense: encode the %, encode a subset of gen-delims but not also encode the sub-delims. For instance this could not replace encodeURIComponent in a C++ version of the following code snippet since if ‘value’ contained ‘&’ or ‘=’ (both sub-delims) they wouldn’t be
encoded and would be confused for delimiters in the name value pairs in the query:
"http://example.com/?key=" + Windows.Foundation.Uri.escapeComponent(value)
Since WsEncodeUrl produces a string URI, to obtain the property they want to encode they’d need to parse the resulting URI. WsDecodeUrl won’t work because it decodes the property but Windows.Foundation.Uri doesn’t
decode. Accordingly the developer could run their string through WsEncodeUrl then Windows.Foundation.Uri to extract the property.
Decode data extracted from URI property
This functionality is available in JavaScript via decodeURIComponent and in C# via System.Uri.UnescapeDataString. Although the two
methods mentioned above will suffice for this purpose, they do not perform exactly the same operation.
Additionally we now also have Windows.Foundation.Uri.UnescapeComponent in WinRT, which is available in JavaScript and C++ (not C# since it doesn’t have access to
Windows.Foundation.Uri). This is also slightly different from the previously mentioned mechanisms but works best for
this purpose.
Decoding is necessary when extracting data from a parsed URI property. For example, if a URI query contains a series of name and value pairs
delimited by ‘=’ between names and values, and by ‘&’ between pairs, one must first parse the query into name and value entries and then decode the values. It is necessary to make this an extra step separate from parsing the URI property so that sub-delimiters (in this case ‘&’ and ‘=’) that are encoded will
be interpreted as data, and those that are decoded will be interpreted as delimiters.
If a developer does not have this API provided they can write it themselves. Percent-decoding methods appear simple to write, but have some tricky
parts including correctly handling non-US-ASCII, and remembering not to decode .
In the following example, note that if unescapeComponent were called first, the encoded ‘&’ and ‘=’ would be decoded and interfere with the parsing of the name
value pairs in the query.
var uri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/?foo=bar&array=%5B%27%E3%84%93%27%2C%27%26%27%2C%27%3D%27%2C%27%23%27%5D");
uri.query.substr(1).split("&").forEach(
function (keyValueString) {
var keyValue = keyValueString.split("=");
console.log(Windows.Foundation.Uri.unescapeComponent(keyValue[0]) + ": " + Windows.Foundation.Uri.unescapeComponent(keyValue[1]));
// foo: bar
// array: ['ㄓ','&','=','#']
});
WsDecodeUrl (C++)
Since WsDecodeUrl decodes all percent-encoded octets it could be used for general purpose percent-decoding but it takes a URI so would require the dev to construct a stub URI around the string they want to decode. For example they could prefix “http:///#” to their string, run
it through WsDecodeUrl and then extract the fragment property. It is convoluted but will work correctly.
Parse Query
The query of a URI is often encoded as
application/x-www-form-urlencoded which is percent-encoded name value pairs delimited by ‘&’ between pairs and ‘=’ between corresponding names and values.
In WinRT we have a class to parse this form of encoding using
Windows.Foundation.WwwFormUrlDecoder.
The
queryParsed property on
the
Windows.Foundation.Uri class is of this type and created with the query of its Uri:
var uri = Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/?foo=bar&array=%5B%27%E3%84%93%27%2C%27%26%27%2C%27%3D%27%2C%27%23%27%5D");
uri.queryParsed.forEach(
function (pair) {
console.log("name: " + pair.name + ", value: " + pair.value);
// name: foo, value: bar
// name: array, value: ['ㄓ','&','=','#']
});
console.log(uri.queryParsed.getFirstValueByName("array")); // ['ㄓ','&','=','#']
The QueryParsed property is only on Windows.Foundation.Uri and not System.Uri and accordingly is not
available in .NET. However the Windows.Foundation.WwwFormUrlDecoder class is available in C# and can be used manually:
Uri uri = new Uri("http://example.com/?foo=bar&array=%5B%27%E3%84%93%27%2C%27%26%27%2C%27%3D%27%2C%27%23%27%5D");
WwwFormUrlDecoder decoder = new WwwFormUrlDecoder(uri.Query);
foreach (IWwwFormUrlDecoderEntry entry in decoder)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("name: " + entry.Name + ", value: " + entry.Value);
// name: foo, value: bar
// name: array, value: ['ㄓ','&','=','#']
}
Build Query
To build a query of name value pairs encoded as
application/x-www-form-urlencoded there is no WinRT API to do this directly.
Instead a developer must do this manually making use of the code
described in “Encode data for including in URI property”.
In terms of public releases, this property is only in the RC and later builds.
For example in JavaScript a developer may write:
var uri = new Windows.Foundation.Uri("http://example.com/"),
query = "?" + Windows.Foundation.Uri.escapeComponent("array") + "=" + Windows.Foundation.Uri.escapeComponent("['ㄓ','&','=','#']");
console.log(uri.combine(new Windows.Foundation.Uri(query)).absoluteUri); // http://example.com/?array=%5B'%E3%84%93'%2C'%26'%2C'%3D'%2C'%23'%5D
 Amazon doesn't say how it determines friendship because that exposes work around or
because we would be creeped out? https://twitter.com/niftyc/status/618275252049608704 …
Amazon doesn't say how it determines friendship because that exposes work around or
because we would be creeped out? https://twitter.com/niftyc/status/618275252049608704 …
 The NSA does not have "an absolute right to gain access to every way in which two
people may choose to communicate." http://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2015/04/nsa-dreams-of-smartphones-with-split-crypto-keys-protecting-user-data/ …
The NSA does not have "an absolute right to gain access to every way in which two
people may choose to communicate." http://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2015/04/nsa-dreams-of-smartphones-with-split-crypto-keys-protecting-user-data/ …
 Naming is important: in Rails you can output raw unescaped HTML with
.safe_html - in React a similar API is called dangerouslySetInnerHTML
Naming is important: in Rails you can output raw unescaped HTML with
.safe_html - in React a similar API is called dangerouslySetInnerHTML
 RE: anti @WordPress "There are 2 types of
programming languages: the ones ppl complain about and the ones nobody uses." -Bjarne Stroustrop
RE: anti @WordPress "There are 2 types of
programming languages: the ones ppl complain about and the ones nobody uses." -Bjarne Stroustrop
 Magazines are trying to create new categories of “super-subscribers” http://nie.mn/1DUg1f8
Magazines are trying to create new categories of “super-subscribers” http://nie.mn/1DUg1f8