Last Thursday I saw a bunch of college friends that I hadn't seen in a while, despite all of us working at Microsoft, and Saul and Ciera who were visiting. We had dinner at Typhoon! which I haven't been to in quite a while. Daniil and Val brought their cute child. I got to see Charlie and Matt who I'm not sure I've seen since my 25th birthday. There was much nerdiness. I need to remember to organize such a night myself sometime in near future so I don't have to wait another year to see them.
 On the weekend Sarah and I went out to dinner at Carnegie's, a former
public library in Ballard, Seattle that's now a restaurant. I saw the restaurant's website in Matt's delicious links and thought it looked interesting. The exterior and entryway look like a public
library, but just inside its redone as a sort of modern version of french classical with a bar and two dining rooms. No pictures since my replacement camera only arrived today, but there are
photos available. They serve french cuisine which was good and
not as expensive as I would have expected. An interesting place, although its a bit of a drive and I'm not sure if we'll be going back soon.
On the weekend Sarah and I went out to dinner at Carnegie's, a former
public library in Ballard, Seattle that's now a restaurant. I saw the restaurant's website in Matt's delicious links and thought it looked interesting. The exterior and entryway look like a public
library, but just inside its redone as a sort of modern version of french classical with a bar and two dining rooms. No pictures since my replacement camera only arrived today, but there are
photos available. They serve french cuisine which was good and
not as expensive as I would have expected. An interesting place, although its a bit of a drive and I'm not sure if we'll be going back soon.
I just upgraded to the Zune 3.0 software which includes games and purchasing music on the Zune via WiFi and once again I'm thrilled that the new firmware is available for old Zunes like mine. Rooting around looking at the new features I noticed Zune Badges for the first time. They're like Xbox Achievements, for example I have a Pixies Silver Artist Power Listener award for listening to the Pixies over 1000 times. I know its ridiculous but I like it, and now I want achievements for everything.
Achievements everywhere would require more developments in self-tracking. Self-trackers, folks who keep statistics on exactly when and what they eat, when and how much they exercise, anything one may track about one's self, were the topic of a Kevin Kelly Quantified Self blog post (also check out Cory Doctorow's SF short story The Things that Make Me Weak and Strange Get Engineered Away featuring a colony of self-trackers). For someone like me with a medium length attention span the data collection needs to be completely automatic or I will lose interest and stop collecting within a week. For instance, Nike iPod shoes that keep track of how many steps the wearer takes. I'll also need software to analyze, display, and share this data on a website like Mycrocosm. I don't want to have to spend extreme amounts of time to create something as wonderful as the Feltron Report (check out his statistic on how many daily measurements he takes for the report). Once we have the data we can give out achievements for everything!

|
Carnivore Eat at least ten different kinds of animals. |

|
Make Friends Meet at least 10% of the residents in your home town. |

|
Globetrotter Visit a city in every country. |

|
You're Old Survive at least 80 years of life. |
Of course none of the above is practical yet, but how about Delicious achievements based on the public Delicious feeds? That should be doable...
Internet Explorer 8 Beta 2 is now available! Some of the new features from this release that I really enjoy are Tab Grouping, the new address-bar, and InPrivate Subscriptions.
Tab Grouping groups tabs that are opened from the same page. For example, on a Google search results page if you open the first two links the two new tabs will be grouped with the Google search results page. If you close one of the tabs in that group focus goes to another tab in that group. Its small, but I really enjoy this feature and without knowing exactly what I wanted while using IE7 and FF2 I knew I wanted something like this. Plus the colors for the tab groups are pretty!
The new address bar and search box makes life much easier by searching through my browsing history for whatever I'm typing in. Other things are searched besides history but since I ignore favorites and use Delicious I mostly care about history. At any rate its one of the things that makes it impossible for me to go machines running IE7.
InPrivate Subscriptions allows you to subscribe to a feed of URLs from which IE should not download content. This is intended for avoiding sites that track you across websites and could sell or share your personal information, but this feature could be used for anything where the goal is to avoid a set of URLs. For example, phishing, malware sites, ad blocking, etc. etc. I think there's some interesting uses for this feature that we have yet to see.
Anyway, we're another release closer to the final IE8 and I can relax a little more.
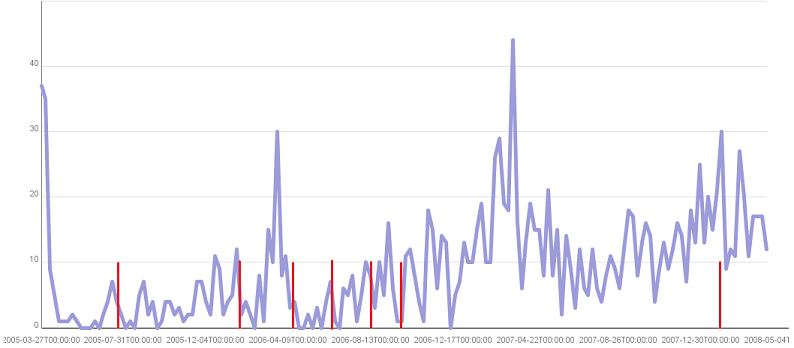
While re-reading Cryptonomicon I thought about what kind of information I'm leaking by posting links on Delicious. At work I don't post any Intranet websites for fear of revealing anything but I wondered if not posting would reveal anything. For instance, if I'm particularly busy at work might I post less indicating something about the state of the things I work on? I got an archive of my Delicious posts via the Delicious API and then ran it through a tool I made to create a couple of tables which I've graphed on Many Eyes


Sarah and I saw the Kids in the Hall "Live As We'll Ever Be" Tour in the WaMu theater in Seattle this past Thursday. I'd only ever seen their television show so it was cool to see them live. I thought that them being in a live format on stage would make the show significantly different, but other than having a bad seat and not being able to see very well, and the Kids sometimes ad-libbing or breaking character, it was like watching their show. It consisted of mostly new material with some returning characters like the Chicken Lady, Buddy Cole, the head crusher, etc. Their Facebook page has two videos that they played during the show.
I've been using the best Kids in the Hall fansite with an archive of searchable transcripts since high school. But now days what with all the new fangled video websites I can link right to some of my favorite sketches from the show. Like the Inexperienced Cannibal.
And the meta-sketch The Raise.
![['Neverending story' by Alexandre Duret-Lutz. A framed photo of books with the droste effect applied. Licensed under creative commons.]](http://farm1.static.flickr.com/90/252757784_3de44cbeb4_m_d.jpg) Information about URI Fragments, the portion of URIs
that follow the '#' at the end and that are used to navigate within a document, is scattered throughout various documents which I usually have to hunt down. Instead I'll link to them all here.
Information about URI Fragments, the portion of URIs
that follow the '#' at the end and that are used to navigate within a document, is scattered throughout various documents which I usually have to hunt down. Instead I'll link to them all here.
Definitions. Fragments are defined in the URI RFC which states that they're used to identify a secondary resource that is related to the primary resource identified by the URI as a subset of the primary, a view of the primary, or some other resource described by the primary. The interpretation of a fragment is based on the mime type of the primary resource. Tim Berners-Lee notes that determining fragment meaning from mime type is a problem because a single URI may contain a single fragment, however over HTTP a single URI can result in the same logical resource represented in different mime types. So there's one fragment but multiple mime types and so multiple interpretations of the one fragment. The URI RFC says that if an author has a single resource available in multiple mime types then the author must ensure that the various representations of a single resource must all resolve fragments to the same logical secondary resource. Depending on which mime types you're dealing with this is either not easy or not possible.
HTTP. In HTTP when URIs are used, the fragment is not included. The General Syntax section of the HTTP standard says it uses the definitions of 'URI-reference' (which includes the fragment), 'absoluteURI', and 'relativeURI' (which don't include the fragment) from the URI RFC. However, the 'URI-reference' term doesn't actually appear in the BNF for the protocol. Accordingly the headers like 'Request-URI', 'Content-Location', 'Location', and 'Referer' which include URIs are defined with 'absoluteURI' or 'relativeURI' and don't include the fragment. This is in keeping with the original fragment definition which says that the fragment is used as a view of the original resource and consequently only needed for resolution on the client. Additionally, the URI RFC explicitly notes that not including the fragment is a privacy feature such that page authors won't be able to stop clients from viewing whatever fragments the client chooses. This seems like an odd claim given that if the author wanted to selectively restrict access to portions of documents there are other options for them like breaking out the parts of a single resource to which the author wishes to restrict access into separate resources.
HTML. In HTML, the HTML mime type RFC defines HTML's fragment use which consists of fragments referring to elements with a corresponding 'id' attribute or one of a particular set of elements with a corresponding 'name' attribute. The HTML spec discusses fragment use additionally noting that the names and ids must be unique in the document and that they must consist of only US-ASCII characters. The ID and NAME attributes are further restricted in section 6 to only consist of alphanumerics, the hyphen, period, colon, and underscore. This is a subset of the characters allowed in the URI fragment so no encoding is discussed since technically its not needed. However, practically speaking, browsers like FireFox and Internet Explorer allow for names and ids containing characters outside of the defined set including characters that must be percent-encoded to appear in a URI fragment. The interpretation of percent-encoded characters in fragments for HTML documents is not consistent across browsers (or in some cases within the same browser) especially for the percent-encoded percent.
Text. Text/plain recently got a fragment definition that allows fragments to refer to particular lines or characters within a text document. The scheme no longer includes regular expressions, which disappointed me at first, but in retrospect is probably good idea for increasing the adoption of this fragment scheme and for avoiding the potential for ubiquitous DoS via regex. One of the authors also notes this on his blog. I look forward to the day when this scheme is widely implemented.
XML. XML has the XPointer framework to define its fragment structure as noted by the XML mime type definition. XPointer consists of a general scheme that contains subschemes that identify a subset of an XML document. Its too bad such a thing wasn't adopted for URI fragments in general to solve the problem of a single resource with multiple mime type representations. I wrote more about XPointer when I worked on hacking XPointer into IE.
SVG and MPEG. Through the Media Fragments Working Group I found a couple more fragment scheme definitions. SVG's fragment scheme is defined in the SVG documentation and looks similar to XML's. MPEG has one defined but I could only find it as an ISO document "Text of ISO/IEC FCD 21000-17 MPEG-12 FID" and not as an RFC which is a little disturbing.
AJAX. AJAX websites have used fragments as an escape hatch for two issues that I've seen. The first is getting a unique URL for versions of a page that are produced on the client by script. The fragment may be changed by script without forcing the page to reload. This goes outside the rules of the standards by using HTML fragments in a fashion not called out by the HTML spec. but it does seem to be inline with the spirit of the fragment in that it is a subview of the original resource and interpretted client side. The other hack-ier use of the fragment in AJAX is for cross domain communication. The basic idea is that different frames or windows may not communicate in normal fashions if they have different domains but they can view each other's URLs and accordingly can change their own fragments in order to send a message out to those who know where to look. IMO this is not inline with the spirit of the fragment but is rather a cool hack.
The move of my website to NearlyFreeSpeech.NET is mostly complete except for a few server side things not working yet: RandomGrammar and parts of Vizicious. I'm still very happy with the NearlyFreeSpeech.NET hosting and so far I've only spent a few cents on hosting. At this rate I'll only spend a few dollars a year.
I've moved all my pages to use the same CSS and hooked it up with cookies to my Kuler color options so now changes to the color theme will stick and apply to all my pages. I haven't figured out the caching for this yet so you may have to refresh to see changes to color applied.
 I signed up for the pre-release beta and purchased a Chumby last year. Chumby looks like a cousin to a GPS
unit. Its similar in size with a touch screen, but has WiFi, accelerometers, and is pillow like on the sides that aren't a screen. In practice its like an Internet alarm clock that shows you photos
and videos off the Web. Its hackable in that Chumby Industries tells you about the various ways to run your own stuff on the Chumby, modifying the boot sequence (it runs Linux), turning on sshd,
etc, etc. The Chumby forum too has lots of info from folks who have found interesting hacks for the device.
I signed up for the pre-release beta and purchased a Chumby last year. Chumby looks like a cousin to a GPS
unit. Its similar in size with a touch screen, but has WiFi, accelerometers, and is pillow like on the sides that aren't a screen. In practice its like an Internet alarm clock that shows you photos
and videos off the Web. Its hackable in that Chumby Industries tells you about the various ways to run your own stuff on the Chumby, modifying the boot sequence (it runs Linux), turning on sshd,
etc, etc. The Chumby forum too has lots of info from folks who have found interesting hacks for the device.
When you turn on the Chumby it downloads and runs the latest version of the Chumby software which lets you set alarms, play music, and display Flash widgets. The Chumby website lets anyone upload their own Flash widgets to share with the community. I tried my hand at creating one using Adobe's free Flash creation SDK but I don't know Flash and didn't have the patience to learn.
Currently my Chumby is set to wake me up at 8am on weekdays with music from ShoutCast and then displays traffic and weather. At 10am everyday it switches to showing me a slide-show of LolCats. At 11pm it switches to night mode where it displays the time in dark grey text on a black background at a reduced light level so as not to disturb me while I sleep.
I like the Chumby but I have two complaints. The first is that it forces me to learn flash in order to create anything cool rather than having a built-in Web browser or depending on a more Web friendly technology. The second complaint is about its name. At first I thought the name was stupid in a kind of silly way, but now that I'm used to the name it sounds vaguely dirty.