![[The cover of Cryptonomicon]](http://images.amazon.com/images/P/0380788624.01._SX140_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg)
![[The cover of Quicksilver]](http://images.amazon.com/images/P/0060593083.01._SX140_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg)
![[The cover of The Confusion]](http://images.amazon.com/images/P/0060733357.01._SX140_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg)
![[The cover of The System of the World]](http://images.amazon.com/images/P/0060750863.01._SX140_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg)
I've finally finished the Baroque Cycle, a historical fiction series set in the 17th and 18th centuries by Neal Stephenson whose work I always enjoy. There were often delays where I'd forget about the books until I had to take plane somewhere, or get discouraged reading about the character's thoughts on economics, or have difficulty finding the next volume, or become more engrossed in other books, projects or video games, and leave the Baroque Cycle books untouched for many months at a time. Consequently, my reading of this series has, I'm ashamed to say, spanned years. After finishing some books which I enjoy I end up hungry for just a bit more to read. For this series I don't need a bit more to read, I'm done with that, but I do want a badge or maybe a medal. Or barring that, college credit in European History and Macro Economics. I can recommend this book to anyone who has enjoyed Neal Stephenson's other work and has a few years of free time to kill.
![['Neverending story' by Alexandre Duret-Lutz. A framed photo of books with the droste effect applied. Licensed under creative commons.]](http://farm1.static.flickr.com/90/252757784_3de44cbeb4_m_d.jpg) Information about URI Fragments, the portion of URIs
that follow the '#' at the end and that are used to navigate within a document, is scattered throughout various documents which I usually have to hunt down. Instead I'll link to them all here.
Information about URI Fragments, the portion of URIs
that follow the '#' at the end and that are used to navigate within a document, is scattered throughout various documents which I usually have to hunt down. Instead I'll link to them all here.
Definitions. Fragments are defined in the URI RFC which states that they're used to identify a secondary resource that is related to the primary resource identified by the URI as a subset of the primary, a view of the primary, or some other resource described by the primary. The interpretation of a fragment is based on the mime type of the primary resource. Tim Berners-Lee notes that determining fragment meaning from mime type is a problem because a single URI may contain a single fragment, however over HTTP a single URI can result in the same logical resource represented in different mime types. So there's one fragment but multiple mime types and so multiple interpretations of the one fragment. The URI RFC says that if an author has a single resource available in multiple mime types then the author must ensure that the various representations of a single resource must all resolve fragments to the same logical secondary resource. Depending on which mime types you're dealing with this is either not easy or not possible.
HTTP. In HTTP when URIs are used, the fragment is not included. The General Syntax section of the HTTP standard says it uses the definitions of 'URI-reference' (which includes the fragment), 'absoluteURI', and 'relativeURI' (which don't include the fragment) from the URI RFC. However, the 'URI-reference' term doesn't actually appear in the BNF for the protocol. Accordingly the headers like 'Request-URI', 'Content-Location', 'Location', and 'Referer' which include URIs are defined with 'absoluteURI' or 'relativeURI' and don't include the fragment. This is in keeping with the original fragment definition which says that the fragment is used as a view of the original resource and consequently only needed for resolution on the client. Additionally, the URI RFC explicitly notes that not including the fragment is a privacy feature such that page authors won't be able to stop clients from viewing whatever fragments the client chooses. This seems like an odd claim given that if the author wanted to selectively restrict access to portions of documents there are other options for them like breaking out the parts of a single resource to which the author wishes to restrict access into separate resources.
HTML. In HTML, the HTML mime type RFC defines HTML's fragment use which consists of fragments referring to elements with a corresponding 'id' attribute or one of a particular set of elements with a corresponding 'name' attribute. The HTML spec discusses fragment use additionally noting that the names and ids must be unique in the document and that they must consist of only US-ASCII characters. The ID and NAME attributes are further restricted in section 6 to only consist of alphanumerics, the hyphen, period, colon, and underscore. This is a subset of the characters allowed in the URI fragment so no encoding is discussed since technically its not needed. However, practically speaking, browsers like FireFox and Internet Explorer allow for names and ids containing characters outside of the defined set including characters that must be percent-encoded to appear in a URI fragment. The interpretation of percent-encoded characters in fragments for HTML documents is not consistent across browsers (or in some cases within the same browser) especially for the percent-encoded percent.
Text. Text/plain recently got a fragment definition that allows fragments to refer to particular lines or characters within a text document. The scheme no longer includes regular expressions, which disappointed me at first, but in retrospect is probably good idea for increasing the adoption of this fragment scheme and for avoiding the potential for ubiquitous DoS via regex. One of the authors also notes this on his blog. I look forward to the day when this scheme is widely implemented.
XML. XML has the XPointer framework to define its fragment structure as noted by the XML mime type definition. XPointer consists of a general scheme that contains subschemes that identify a subset of an XML document. Its too bad such a thing wasn't adopted for URI fragments in general to solve the problem of a single resource with multiple mime type representations. I wrote more about XPointer when I worked on hacking XPointer into IE.
SVG and MPEG. Through the Media Fragments Working Group I found a couple more fragment scheme definitions. SVG's fragment scheme is defined in the SVG documentation and looks similar to XML's. MPEG has one defined but I could only find it as an ISO document "Text of ISO/IEC FCD 21000-17 MPEG-12 FID" and not as an RFC which is a little disturbing.
AJAX. AJAX websites have used fragments as an escape hatch for two issues that I've seen. The first is getting a unique URL for versions of a page that are produced on the client by script. The fragment may be changed by script without forcing the page to reload. This goes outside the rules of the standards by using HTML fragments in a fashion not called out by the HTML spec. but it does seem to be inline with the spirit of the fragment in that it is a subview of the original resource and interpretted client side. The other hack-ier use of the fragment in AJAX is for cross domain communication. The basic idea is that different frames or windows may not communicate in normal fashions if they have different domains but they can view each other's URLs and accordingly can change their own fragments in order to send a message out to those who know where to look. IMO this is not inline with the spirit of the fragment but is rather a cool hack.
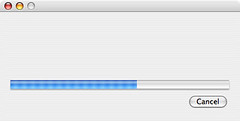 More of my thoughts have been stolen: In my
previous job the customer wanted a progress bar displayed while information was copied off of proprietary hardware, during which the software didn't get any indication of progress until the copy
was finished. I joked (mostly) that we could display a progress bar that continuously slows down and never quite reaches the end until we know we're done getting info from the hardware. The amount
of progress would be a function of time where as time approaches infinity, progress approaches a value of at most 100 percent.
More of my thoughts have been stolen: In my
previous job the customer wanted a progress bar displayed while information was copied off of proprietary hardware, during which the software didn't get any indication of progress until the copy
was finished. I joked (mostly) that we could display a progress bar that continuously slows down and never quite reaches the end until we know we're done getting info from the hardware. The amount
of progress would be a function of time where as time approaches infinity, progress approaches a value of at most 100 percent.
This is similar to Zeno's Paradox which says you can't cross a room because to do so first you must cross half the room, then you must cross half the remaining distance, then half the remaining again, and so on which means you must take an infinite number of steps. There's also an old joke inspired by Zeno's Paradox. The joke is the prototypical engineering vs sciences joke and is moderately humorous, but I think the fact that Wolfram has an interactive applet demonstrating the joke is funnier than the joke itself.
I recently found Lou Franco's blog post "Using Zeno's Paradox For Progress Bars" which covers the same concept as Zeno's Progress Bar but with real code. Apparently Lou wasn't making a joke and actually used this progress bar in an application. A progress bar that doesn't accurately represent progress seems dishonest. In cases like the Vista Defrag where the software can't make a reasonable guess about how long a process will take the software shouldn't display a progress bar.
Similarly a paper by Chris Harrison "Rethinking the Progress Bar" suggests that if a progress bar speeds up towards the end the user will perceive the operation as taking less time. The paper is interesting, but as in the previous case, I'd rather have progress accurately represented even if it means the user doesn't perceive the operation as being as fast.
Update: I should be clearer about Lou's post. He was actually making a practical and implementable suggestion as to how to handle the case of displaying progress when you have some idea of how long it will take but no indications of progress, whereas my suggestion is impractical and more of a joke concerning displaying progress with no indication of progress nor a general idea of how long it will take.
 I now have search and an archive available for my site. I previously tried to setup crappy search by cheating using Yahoo Pipes and now
instead I have a slightly less crappy search that works over all of the content that I've produced on my blog, uploaded to flickr or youtube, or added to delicious.
I now have search and an archive available for my site. I previously tried to setup crappy search by cheating using Yahoo Pipes and now
instead I have a slightly less crappy search that works over all of the content that I've produced on my blog, uploaded to flickr or youtube, or added to delicious.
You can now read my first LiveJournal blog post or, for probably much more entertainment value, view all the photos and videos of Cadbury by searching for 'bunny'.
The search is only slightly less lame because although it searches over all my content, I still implemented it myself rather than getting a professional package. Also, the feed supports the same search and archive as my homepage so you can subscribe to a feed of Cadbury if you're so inclined and just skip all this other boring stuff. My homepage and feed implement the OpenSearch response elements and I've got an OpenSearch search provider (source) as well.
Internet Explorer 8 has made my plugin Feed Folder obselete in functionality and implementation -- which is good!
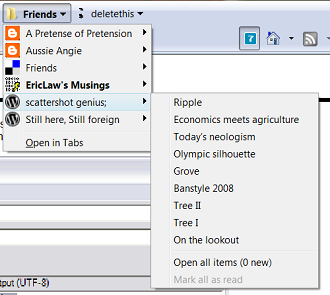
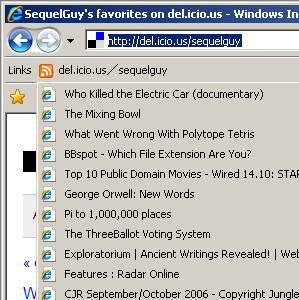
I made Feed Folder for IE7 because I wanted the Live Bookmarking feature from FireFox. The Feed Folder plugin for IE7 would allow you to display your feeds as virtual folders in your Links Bar. When your feed is updated the virtual folder is updated as well with the new feed items. I use del.icio.us to store all my links so I could add virtual folders of my daily links, my friends blogs links, quick reference links, etc. etc.
My plugin relied on shell folders to implement the virtual folders I described above, but IE8 doesn't support shell folders in the Favorites Bar. But I'm OK with Feed Folder not working in IE8 since there's a much better implementation already there. IE8 does better than my plugin on a number of points: First, there isn't the horrible perf. issue that my plugin had on Vista. Second, when a feed is updated the virtual folder flashes to note the change in status. Third, unread items are bolded and the bolding bubbles up from feeds contained in subfolders. And lastly, the middle click button is supported to open items in a new tab.
Accordingly, I don't plan to work on Feed Folder anymore unless someone comes up with a good reason. Instead I mark Feed Folder deprecated and suggest you use Internet Explorer 8 instead.
To use this feature in IE8 simply drag a feed from your feed list in your Favorites Center onto your Favorites Bar. Or, when viewing a feed, click on the 'Add to Favorites' Star Plus icon thing in the upper left, and select 'Monitor on Favorites Bar'. A .url Internet Shortcut file is produced as usual, but if you open up the .url file you'll see there's some additional info about the feed.
![[Many books in large bookcase. Photo creator http://flickr.com/people/babblingdweeb/]](http://farm1.static.flickr.com/18/23816128_d4acb70b2d_m_d.jpg) I use my recently added
books feed from LibraryThing, a site I've mentioned before where you track, review, recommend, and share your books, and I put the recently added
books on my page. I thought it might be nice to include the book covers so I suggested adding book covers to RSS feeds in
LibraryThings 'Recommend Site Improvements' group. The next day I had a response from the founder and lead developer Tim Spalding who
had started implementing the feature. I noticed a few bugs, reported them on the same thread, and he fixed them soon after. Fantastic! It makes me want to upgrade to a paying account.
I use my recently added
books feed from LibraryThing, a site I've mentioned before where you track, review, recommend, and share your books, and I put the recently added
books on my page. I thought it might be nice to include the book covers so I suggested adding book covers to RSS feeds in
LibraryThings 'Recommend Site Improvements' group. The next day I had a response from the founder and lead developer Tim Spalding who
had started implementing the feature. I noticed a few bugs, reported them on the same thread, and he fixed them soon after. Fantastic! It makes me want to upgrade to a paying account.
Incidentally, if you notice the Ghost in the Shell book appear multiple times in my RSS feed its due to the previously mentioned iterative bug fixes. The same item appeared multiple times slightly differently with each bug fix and your RSS aggregator may have picked them up as distinct items.